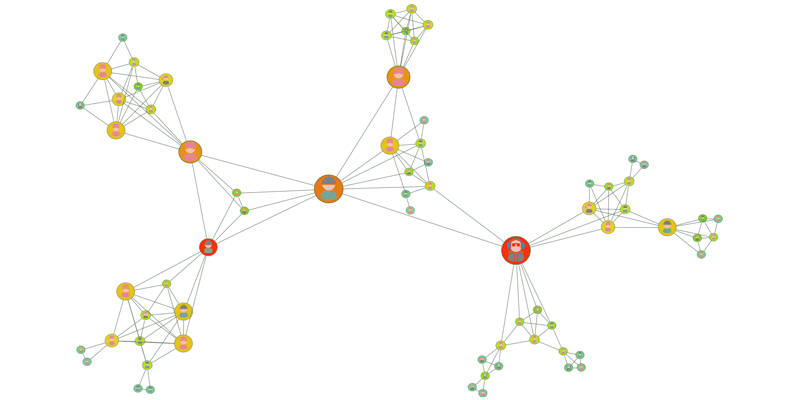
What is graph intelligence?
Graph intelligence refers to the application of analytical and computational techniques to extract insights from graph data structures. It involves analyzing relationships and patterns within networks, where entities are represented as nodes and their connections as edges. This approach is critical in areas like social network analysis, bioinformatics, supply chain management, and fraud detection.
Graph intelligence leverages algorithms to understand complex interdependencies, identify clusters, and predict trends in networked data, offering deeper insights than traditional linear data analysis methods.
Graph intelligence can help you:
- Discover areas of interest in data
- Optimize complex systems or processes
- Deliver key information to stakeholders and decision makers in a timely manner
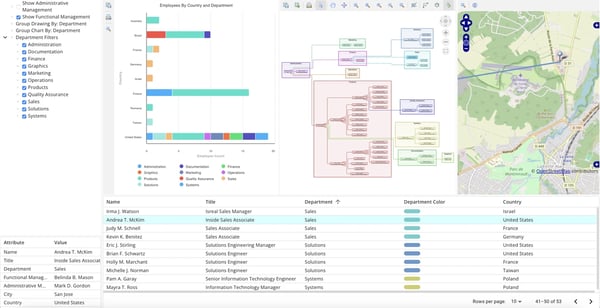
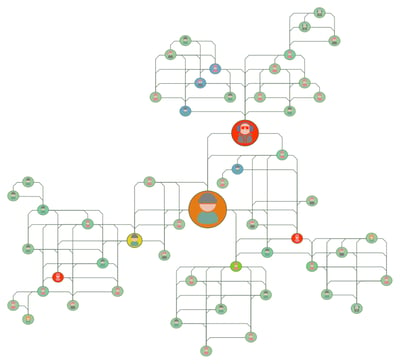
A graph intelligence dashboard for company organizational management.
Whatever your goals are with data, using graph intelligence to understand which nodes or edges are more important than others is key for gaining value and intelligence from data.
Why is graph intelligence important?
Graph intelligence is crucial because it enables a deeper understanding of complex relationships and structures in data. It transforms complex data into actionable insights and turns your data into knowledge, making it a valuable tool in today's data-driven world.
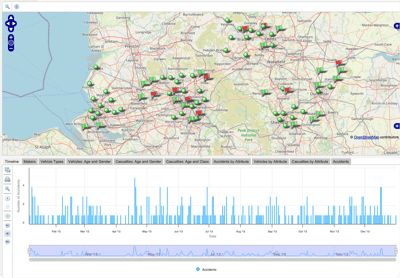
Graph intelligence enables intelligence analysts to take action on their data.
Uncover Hidden Patterns
Graph intelligence reveals intricate and often hidden connections within large datasets.
Discover Key Relationships
Graph intelligence highlights relationships enabling discovery of key relationships in your data.
Enhance Decision-Making
Graph intelligence provides insights that enhance communication of results to stakeholders and leads to more informed decisions.
Predict Trends and Behaviors
Graph intelligence network analysis can forecast future trends and behaviors providing powerful insight for your business.
Optimize Networks
Graph intelligence identifies inefficiencies and opportunities in networked systems like supply chains, communication networks, or social networks.
Detect Anomalies
Graph intelligence aids in the detection of unusual patterns, which is valuable in fraud detection and security.
Core components of graph intelligence
Graph intelligence is multifaceted. There are a number of fundamental elements that make up the foundation of graph intelligence. It is important for anyone planning to use graph intelligence to gain an understanding of its complexities and capabilities.
Nodes and edges: The basic building blocks
Nodes and edges are the foundation of graph intelligence. Nodes represent entities in the network, for example, people, places, and things. Edges represent relationships or interactions between nodes in networks, fraud rings, organizational hierarchies, and more. Paths that use a sequence of edges to connect two nodes can show indirect, yet important, relationships.
Databases and data integration
Data can reside in a graph database, which is designed to efficiently store and manage graph data. However, data may reside in a relational database or a text-based format. Often, data may be located across several different types of data stores, requiring federation of the data for effective analysis. Data integration and federation combine data from various sources to enrich the graph and enable deeper insight considering multiple facets.
Graph visualization
Graph visualization visually represents the network of nodes and edges, and is vital to understanding the graph structures and patterns in data. Effective graph visualization can provide flexibility in how nodes and edges are represented, such as customizable node and edge UIs. A dashboard view of graph and data visualizations can aggregate information into a centralized view of information, enabling users to see a snapshot of all key information at once, for increased efficiency and time-saving.
Graph analysis algorithms
Graph analytics help analysts find what is important in the data. Graph analysis techniques include traversals, clustering, partitioning, path, cycle, social network, network flow, and tree analysis algorithms. Graph analysis helps find important patterns, discover areas of interest in data, optimize complex systems or processes, determine root cause, and more.
Interactive graph navigation
Interactive graph navigation enables exploration of data in real-time, and facilitates discovery. It also enables analysts to focus on the parts of the data that they are interested in, without being distracted by extraneous information. Interaction techniques can include expanding and collapsing of nested drawings to show more or less detail, and drilling in or out to focus on a particular graph or sub-graph.
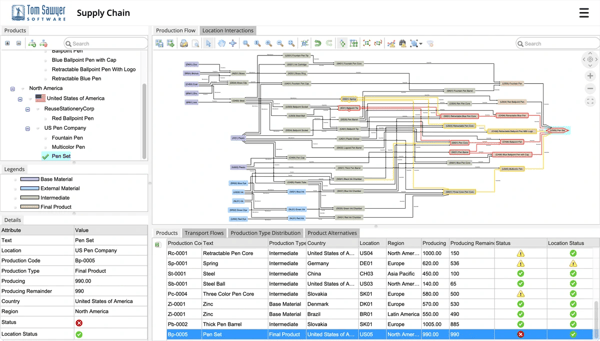
Graph intelligence for supply chain management.
Who can benefit from graph intelligence?
Graph intelligence is applicable to industries in the private and public sectors. Data analysts and data scientists rely on graph analytics to solve big data problems in digital transformation, digital engineering, supply chain, logistics, social network analysis, and fraud detection and prevention.
Graph intelligence is impactful in many industries where having up-to-the-minute information is crucial and decisions have major consequences:
- Manufacturing
- Law Enforcement
- IT
- Banking
- Insurance
- Government
Steps for graph intelligence implementation
To have best results in applying graph intelligence to problems, analysts must:
- Have a clear use case
- Identify and gather the various sources of data for analysis
- Use effective graph visualization tools to interpret, navigate, and communicate insights
- Apply the appropriate set of graph intelligence analytics
- Focus on the most relevant data
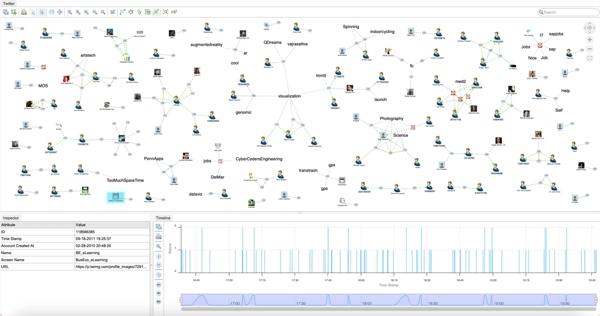
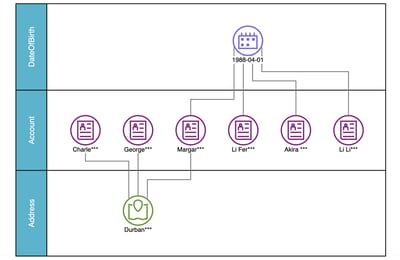
The application of graph intelligence tailored for a specific use case.
Technical challenges of getting started with graph intelligence
Graph intelligence analysts must surmount several obstacles in order to discover important insights.
First, analysts often are not sure exactly how to apply graph technology to their data. And, when they do start to use graph technology, they may apply techniques that are not the best for their use case. For example, someone new to graph intelligence may look for direct connections instead of also searching for paths, which are useful for discovering more relationships.
Poor visualization or analysis that is not powerful enough for the use case also hampers the understanding of results and navigation of data. And an additional challenge is collecting of graph analytics without context that explains their meaning and defines their importance.
Analysts need effective and easy-to-use graph intelligence technology that provides necessary graph tools. This platform must provide:
- Ability to connect to many types of data sources, including graph databases and relational databases
- High-precision graph visualizations that can be used for complex data
- Efficient graph compute
- Effective data navigation
- Dashboards for communication of results to stakeholders and decision makers
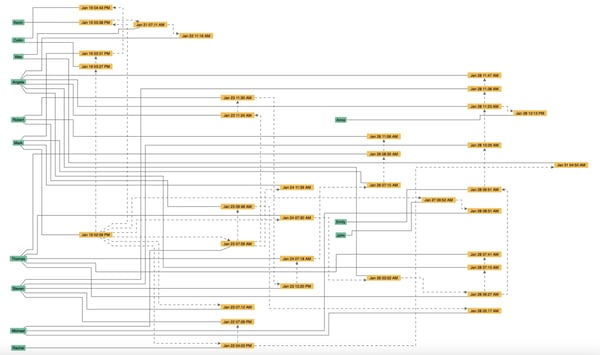
Use graph intelligence to understand important paths in your data.
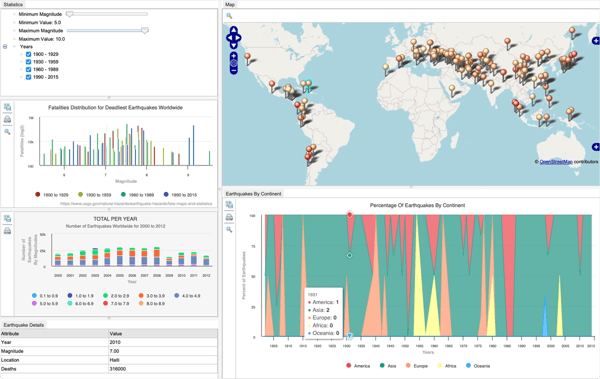
Navigate to relevant data with the assistance of graph intelligence.
Graph technology to enhance intelligence analysis
Graph Layout
Perspectives provides best-in-class graph layout to create useful and readable visualizations of complex data.
Graph Analytics
Perspectives graph analytics library provides graph intelligence algorithms that can be run in real-time through automated background processes, or interactively by users.
Query Builder
Perspectives advanced, visual query builder allows you to search for matching patterns in your graphs to load data from triple stores and labeled property graphs alike without the need to know SPARQL, Gremlin, or Cypher query languages.
Load Neighbors
Perspectives load neighbors feature with advanced pattern matching provides analysts control over the data they see to support efficient navigation of data during intelligence gathering.

Timeline
Perspective's timeline view helps analysts see when key events occurred adding context to their analysis.
Filters
Perspectives filters provide a way for analysts to focus on key results.
Swimlanes
Perspectives swimlanes add at-a-glance categorization of data elements.
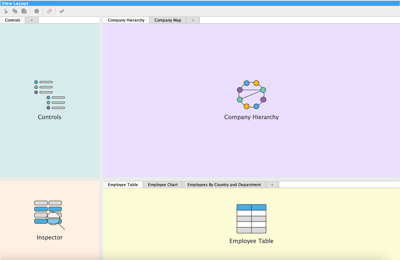
View Layout
With Perspectives, you can create dashboards tailored for your use case and stakeholders in minutes.
User interaction and data retrieval
An important aspect of graph intelligence is how users engage with graph-based systems and how these systems fetch and display data. The ability to interact with data and analytics results provides more useful explorations through data and allows intelligence analysts to discover additional insights in real-time.
This navigation through data is supported by populating the data model from any data source, whether graph, relational, or text-based data sources, and an application with a user-friendly interface that provides tools for analysts to build queries and interactively load data.
Query builder: A tool for structured data retrieval
For successful interaction, analysts must be able to construct complex queries to retrieve specific data from a graph database. The Perspectives query builder simplifies accessing targeted information from triple stores and labeled property graphs alike through a user-friendly interface, without the need for the analysts to know a technical query language. Users can specify criteria, relationships, and attributes to filter and retrieve data efficiently and effectively, or use advanced pattern matching to create visual patterns and search for connectivity patterns in data. The ability to efficiently create targeted queries enables precise data extraction from complex network structures, and facilitates advanced analysis and decision-making.

The Pattern Matching Query Builder simplifies accessing targeted information through a user-friendly graph visualization.
Data navigation: The mechanism for exploring network structures
Methodologies and tools that enable intelligence analysts to intuitively traverse and understand complex network structures include techniques such as filtering, searching, and clustering algorithms, which allow users to focus on specific parts of the graph. Graph intelligence platforms such as Perspectives employs dynamic layouts and responsive design elements that adjust to user interactions, making the exploration of large and intricate networks manageable and insightful. With effective data navigation, analysts are able to effectively navigate and decipher the wealth of information embedded in graph data.

Filtering data allow users to interact with and focus on specific parts of the graph.
Data interaction: User-system interface in graph intelligence systems
User-friendly interfaces allow intuitive exploration of complex graph data. Interactive elements like zooming, panning, and clicking on nodes and edges for detailed information, and more advanced interaction like expanding, collapsing, hiding, and showing nodes is essential. In addition, effective graph visualization and highlighting of analytics results are necessary for graph intelligence software so that intelligence analysts can focus on key parts of the data and communicate key findings.
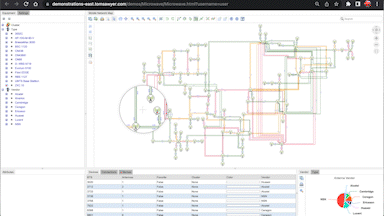
User interaction is an important aspect of graph intelligence.
Gathering your data into a single model
Creating a graph data model tailored to your use case is key to discovering important results. This begins with the definition of a schema to understand the type of data and attributes that will be analyzed.
It is common for data to be contained in any number of different data stores, either graph databases or non-graph data sources, such as SQL, RESTful endpoints, JSON, XML, Excel, and structured text files.
The Tom Sawyer Perspectives graph intelligence platform is data agnostic so that you can build a single schema and apply graph technology to data no matter where it resides. It meets the needs of intelligence analysts by providing a way to import data, perform graph compute, see results, and load related data.
Supported data sources include:

Perspectives supports data federation and integration from a wide range of data sources.
Types of graphs used in intelligence
The types of graphs used in intelligence range from simple undirected graphs to complex hierarchical and multilayered structures. Each graph type may be suited to different analytical needs and scenarios. Understanding these variations is crucial for effectively applying graph intelligence in real-world problems, enhancing the clarity and precision of data interpretation.
The different graph types are as follows:
- Simple Undirected Graphs: Ideal for modeling symmetric relationships where the direction of connection is irrelevant, like mutual friendships in social networks.
- Directed Graphs: Useful in scenarios where the direction of relationships matters, such as in web link structures or supply chains.
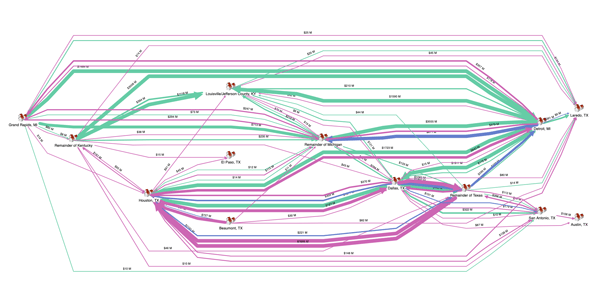
- Weighted Graphs: Employed when relationships have varying strengths or capacities, like in traffic networks or resource flow analysis.
- Hierarchical Graphs: Suited for representing data with inherent hierarchical structures, such as organizational charts or taxonomies.
- Multilayered Graphs: Effective in complex scenarios involving multiple types of relationships or interactions, such as in multifaceted social networks or interconnected systems spanning different domains.
Each type provides a unique lens for examining and interpreting specific aspects of interconnected data.
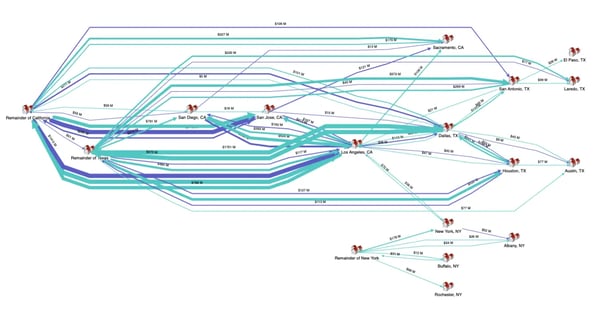
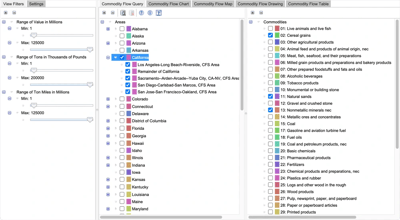
Weighted graph showing relationships of varying strength in the flow of commodities.
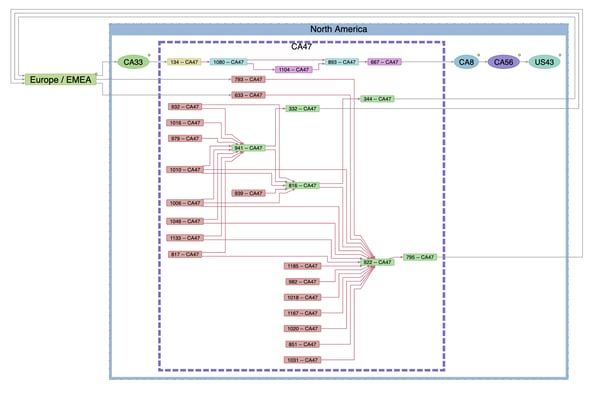
Directed graph of a supply chain.
Applications of graph intelligence
Graph intelligence applications include those used in:
Investigation and Policing
Network Analysis
Systems Engineering
Logistics
Supply Chain
Life sciences
Advertising and Entertainment
Built using Tom Sawyer Perspectives, the following example graph intelligence applications showcase what's possible with Perspectives. Sign up and explore.
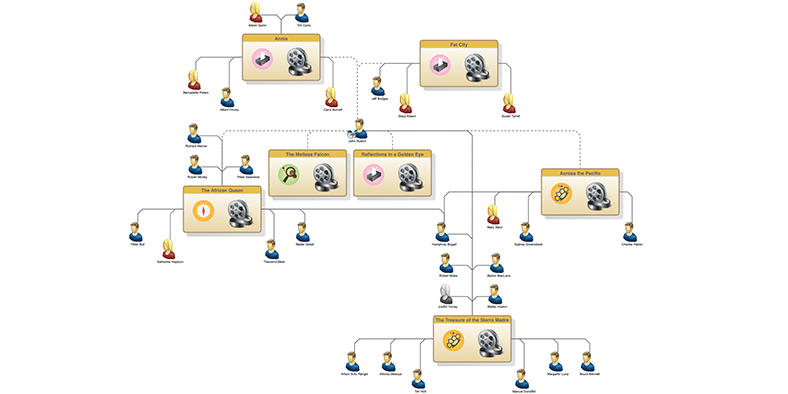
Cineasts
TECHNOLOGIES
Copyright © 2026 Tom Sawyer Software. All rights reserved. | Terms of Use | Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2026 Tom Sawyer Software.
All rights reserved. | Terms of Use | Privacy Policy